A dangerous malware threat has emerged targeting Windows users across Korea through webhard file-sharing services.
The Ahnlab Security Intelligence Center recently identified xRAT, also known as QuasarRAT, being distributed as fake adult games to unsuspecting users.
This remote access trojan represents a significant security concern for Windows systems, combining sophisticated evasion techniques with social engineering tactics that make it particularly dangerous to everyday users.
The malware takes advantage of webhard services, which are extremely popular in Korea for distributing content.
Threat actors exploit this platform’s accessibility by uploading compressed files disguised as innocent games and adult content.
Users see what appears to be legitimate game downloads but instead receive malicious files hidden behind attractive file names and descriptions.
This deception strategy has proven highly effective, allowing attackers to compromise systems without raising user suspicion during the initial download phase.

ASEC analysts identified that multiple similar distributions occurred through the same threat actor, suggesting a coordinated campaign.
Although many posts were deleted by the time of analysis, investigators confirmed that numerous games shared identical malware payloads.
Infection and Persistence Mechanism
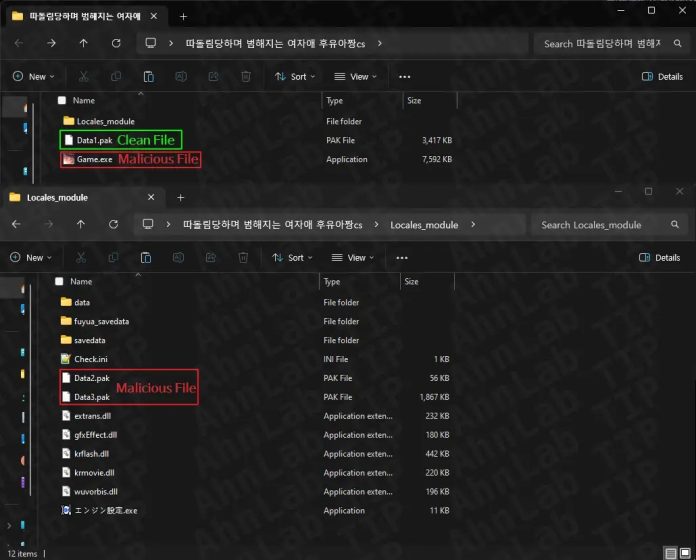
The technical structure of this attack reveals sophisticated engineering. When users download the malware, they receive a ZIP file containing multiple components including Game.exe, Data1.Pak, and supporting files.
Upon execution, Game.exe acts as a launcher rather than an actual game application.
When users click the play button, the malware copies Data1.Pak to the Locales_module folder as Play.exe, while simultaneously deploying Data2.Pak and Data3.Pak to the Windows Explorer directory path as GoogleUpdate.exe and WinUpdate.db respectively.
The infection chain becomes more complex when GoogleUpdate.exe executes. It searches for WinUpdate.db in the same directory and applies AES encryption decryption to extract the final shellcode.
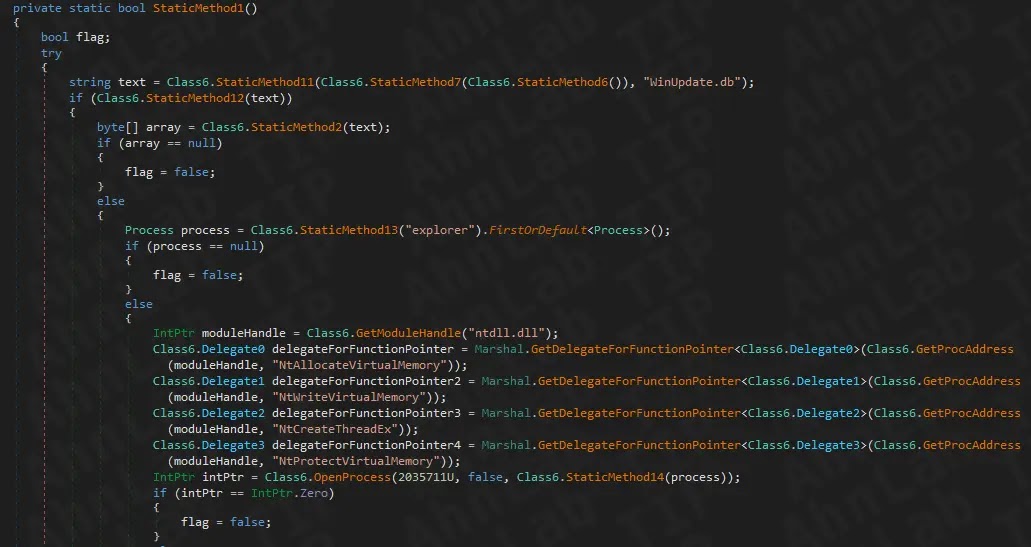
This shellcode gets injected into explorer.exe, a critical Windows process, allowing the malware to operate with elevated privileges.
Notably, the malware patches the EtwEventWrite function in explorer.exe with a specific return instruction, effectively disabling Event Tracing for Windows logging.
This persistence technique prevents security tools and administrators from detecting malicious activity through standard event logs.
The final injected code is the actual xRAT payload, which performs dangerous operations including system information collection, keyboard monitoring, and unauthorized file transfers.
Security professionals recommend downloading programs exclusively from official sources and exercising extreme caution when accessing file-sharing websites to prevent such infections.
Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X to Get More Instant Updates, Set CSN as a Preferred Source in Google.
The post xRAT Malware Attacking Windows Users Disguised as Adult Game appeared first on Cyber Security News.