A coordinated campaign is using malicious Chrome extensions that impersonate popular AI tools like ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, and Grok.
These fake “AI assistants” spy on users through injected, remote-controlled iframes, turning helpful browser add-ons into surveillance tools. More than 260,000 users have installed these extensions.
Security researchers identified at least 30 Chrome extensions promoted as AI tools for summarizing, chatting, translating, generating images, and boosting Gmail productivity.
Although they use different names and icons, they share the same codebase, permissions, and backend infrastructure, confirming a single organized operation.
Some extensions were even marked as “Featured” in the Chrome Web Store, increasing trust and downloads.
Here is the malicious extensions table in a clean format:
| Extension ID | Name | Installs |
|---|---|---|
| nlhpidbjmmffhoogcennoiopekbiglbp | AI Assistant | 50,000 |
| gcfianbpjcfkafpiadmheejkokcmdkjl | Llama | 147 |
| fppbiomdkfbhgjjdmojlogeceejinadg | Gemini AI Sidebar | 80,000 |
| djhjckkfgancelbmgcamjimgphaphjdl | AI Sidebar | 9,000 |
| llojfncgbabajmdglnkbhmiebiinohek | ChatGPT Sidebar | 10,000 |
| gghdfkafnhfpaooiolhncejnlgglhkhe | AI Sidebar | 50,000 |
| cgmmcoandmabammnhfnjcakdeejbfimn | Grok | 261 |
| phiphcloddhmndjbdedgfbglhpkjcffh | Asking Chat Gpt | 396 |
| pgfibniplgcnccdnkhblpmmlfodijppg | ChatGBT | 1,000 |
| nkgbfengofophpmonladgaldioelckbe | Chat Bot GPT | 426 |
| gcdfailafdfjbailcdcbjmeginhncjkb | Grok Chatbot | 225 |
| ebmmjmakencgmgoijdfnbailknaaiffh | Chat With Gemini | 760 |
| baonbjckakcpgliaafcodddkoednpjgf | XAI | 138 |
| fdlagfnfaheppaigholhoojabfaapnhb | Google Gemini | 7,000 |
| gnaekhndaddbimfllbgmecjijbbfpabc | Ask Gemini | 1,000 |
| hgnjolbjpjmhepcbjgeeallnamkjnfgi | AI Letter Generator | 129 |
| lodlcpnbppgipaimgbjgniokjcnpiiad | AI Message Generator | 24 |
| cmpmhhjahlioglkleiofbjodhhiejhei | AI Translator | 194 |
| bilfflcophfehljhpnklmcelkoiffapb | AI For Translation | 91 |
| cicjlpmjmimeoempffghfglndokjihhn | AI Cover Letter Generator | 27 |
| ckneindgfbjnbbiggcmnjeofelhflhaj | AI Image Generator Chat GPT | 249 |
| dbclhjpifdfkofnmjfpheiondafpkoed | Ai Wallpaper Generator | 289 |
| ecikmpoikkcelnakpgaeplcjoickgacj | Ai Picture Generator | 813 |
| kepibgehhljlecgaeihhnmibnmikbnga | DeepSeek Download | 275 |
| ckicoadchmmndbakbokhapncehanaeni | AI Email Writer | 64 |
| fnjinbdmidgjkpmlihcginjipjaoapol | Email Generator AI | 881 |
| gohgeedemmaohocbaccllpkabadoogpl | DeepSeek Chat | 1,000 |
| flnecpdpbhdblkpnegekobahlijbmfok | ChatGPT Picture Generator | 251 |
| acaeafediijmccnjlokgcdiojiljfpbe | ChatGPT Translate | 30,000 |
| kblengdlefjpjkekanpoidgoghdngdgl | AI GPT | 20,000 |
| idhknpoceajhnjokpnbicildeoligdgh | ChatGPT Translation | 1,000 |
| fpmkabpaklbhbhegegapfkenkmpipick | Chat GPT for Gmail | 1,000 |
How the Extensions Work
When one extension is removed, attackers quickly upload a clone with a new name and ID, a tactic known as “extension spraying.”
Instead of running AI features locally, the extensions load a full-screen iframe from attacker-controlled domains such as tapnetic[.]pro.

This allows operators to change functionality remotely without updating the extension in the Chrome Web Store.
Once installed, the extensions can: Extract readable content from active tabs, including authenticated pages.
Capture voice input using the Web Speech API. Track installs and uninstalls using hidden telemetry. A Gmail-focused cluster of 15 extensions injects scripts directly into mail. google[.]com.
These scripts monitor page changes and repeatedly collect visible email content, including threads, drafts, and replies, and send it to attacker-controlled servers.
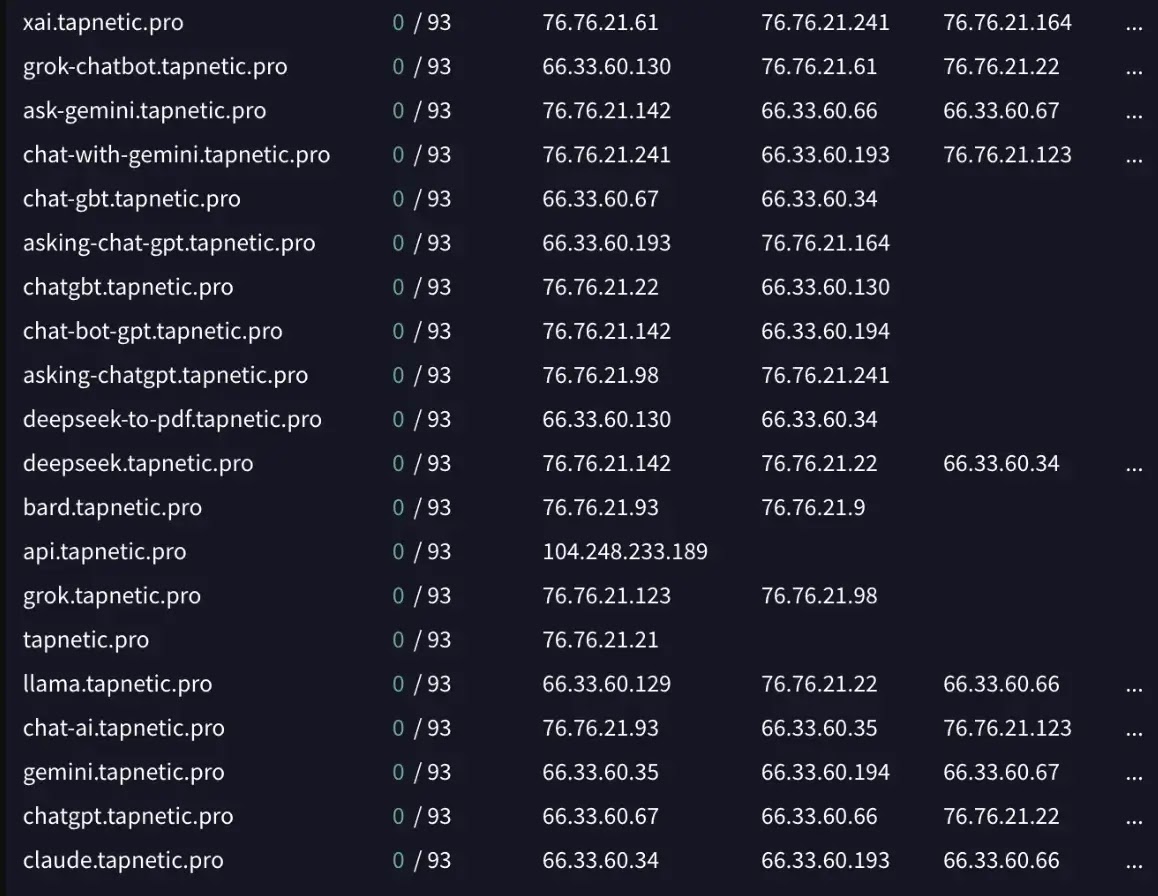
All identified extensions communicate with domains under tapnetic[.]pro and onlineapp[.]pro.
Each extension uses themed subdomains (such as chatgpt. tapnetic[.]pro or gemini. tapnetic[.]pro), but connects to the same backend system.
When one high-install extension was removed in February 2025, an identical replacement appeared within weeks using the same malicious architecture.
According to LayerxSecurity researcher, the campaign also relies on multiple Gmail accounts to manage and publish extensions.
Tactics and Defender Guidance
| Tactic | Technique Code | Technique Name |
|---|---|---|
| Resource Development | LX2.003 (T1583) | Acquire Infrastructure |
| Initial Access | LX3.004 (T1189) | Drive-by Compromise |
| Initial Access | LX3.003 (T1199) | Trusted Relationship |
| Execution | LX4.003 | Script Execution |
| Defense Evasion | LX7.011 (T1036) | Masquerading |
| Credential Access | LX8.007 (T1557) | Adversary-in-the-Middle |
| Collection | LX10.012 | Web Communication Data Collection |
| Collection | LX10.005 | Collect User’s Information |
| Command and Control | LX11.004 | Establish Network Connection |
| Command and Control | LX11.005 | Web Service-Based C2 |
| Exfiltration | LX12.001 | Data Exfiltration |
The operation uses brand impersonation, malicious browser extensions, and web-based command-and-control infrastructure.
By relying on remote iframes, attackers bypass install-time reviews and maintain full control after deployment.
Defenders should: Audit AI-branded Chrome extensions in their environments. Monitor for suspicious iframe injection and unusual Gmail DOM access.
Watch for outbound traffic to tapnetic[.]pro and related domains. Prioritize runtime monitoring over static extension reviews.
Organizations should treat AI-themed browser extensions with caution and enforce strict extension management policies.
Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X for daily cybersecurity updates. Contact us to feature your stories.
The post Malicious Chrome AI Extensions Attacking 260,000 Users via Injected IFrames appeared first on Cyber Security News.